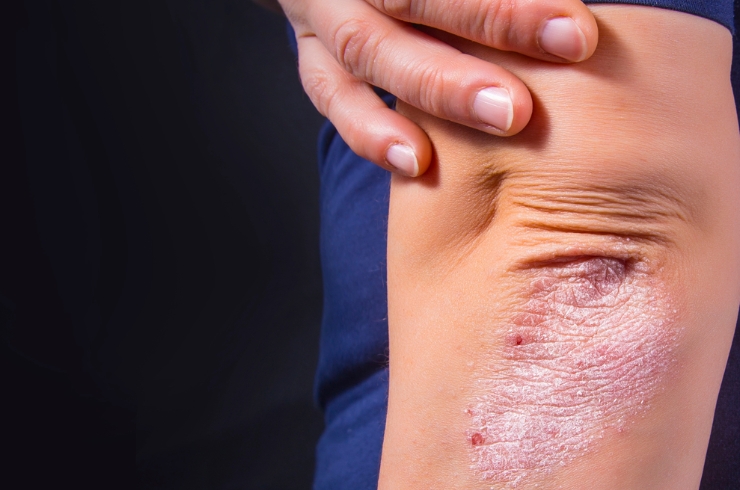
Understanding Psoriasis: A Chronic Skin Disorder with Profound Impacts
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder characterized by the accelerated production of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick, scaly, and inflamed patches. This persistent condition disrupts the life cycle of skin cells, causing them to accumulate rapidly on the skin’s surface, manifesting as silvery-white scales and red, itchy lesions. The severity of psoriasis varies among individuals, ranging from mild nuisance-level patches to severe, debilitating outbreaks that can significantly affect quality of life. While the exact cause of psoriasis remains elusive, it is widely believed to result from a complex interplay of genetic predisposition, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers. Factors such as stress, poor diet, lack of physical activity, hormonal imbalances, and exposure to pollutants contribute to the exacerbation of symptoms. Although psoriasis is not contagious, its visible manifestations can lead to social stigma, emotional distress, and even depression, making holistic management essential. While there is no absolute cure, lifestyle modifications, dietary interventions, and natural treatment protocols can help in alleviating symptoms and achieving prolonged remission.
Diverse Types of Psoriasis and Their Unique Manifestations
Psoriasis manifests in several distinct forms, each exhibiting unique characteristics and varying degrees of severity. Plaque Psoriasis, the most common type, appears as raised, inflamed patches covered with silvery scales, commonly found on the knees, elbows, and scalp. Guttate Psoriasis presents as small, drop-like pink lesions, typically triggered by bacterial infections and often affecting children and young adults. Inverse Psoriasis, characterized by smooth, red, and inflamed lesions, commonly develops in skin folds such as under the breasts, around the genitals, and in the armpits. Pustular Psoriasis, a more severe form, results in white pustules filled with pus, accompanied by widespread redness and scaling. Erythrodermic Psoriasis, the rarest and most aggressive variant, causes intense redness, inflammation, and peeling over large areas of the body, often accompanied by fever and severe discomfort. Nail Psoriasis affects the fingernails and toenails, leading to pitting, discoloration, and structural deformities, while Psoriatic Arthritis causes joint inflammation and deformities, significantly impacting mobility. Each type of psoriasis demands a tailored approach to treatment, incorporating dietary corrections, stress management, immune modulation, and detoxification to mitigate symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Holistic Treatment Protocol: A Natural Path to Healing
A comprehensive, holistic approach to psoriasis focuses on detoxification, immune regulation, and lifestyle adjustments to restore internal balance. Avoiding allergenic and inflammatory foods, such as processed sugars, dairy, and gluten, is crucial in reducing immune system overactivity. Optimizing digestive health through the regulation of the biological clock, consuming gut-friendly foods, and ensuring proper nutrient absorption plays a pivotal role in alleviating symptoms. Detoxifying vital organs like the liver, kidneys, and colon through natural chelation methods enhances the body’s ability to eliminate toxins and maintain a healthy acid-alkali balance. Supplementing with phytonutrients, antioxidants, and essential vitamins ensures cellular nourishment and strengthens immune resilience. Physical exercise, yoga, and mindfulness practices further accelerate the healing process by reducing stress levels and enhancing blood circulation. Patients often experience visible improvements within weeks, with optimal recovery occurring over four to six months. The holistic approach not only addresses psoriasis but also rejuvenates overall well-being, leading to enhanced energy levels, improved digestion, better skin health, and long-term disease management. With a dedicated commitment to natural healing, individuals can regain control over their condition and enjoy a healthier, more fulfilling life free from the burden of psoriasis.
